FGD (Complete Flue Gas Treatment)
Our niche expertise and a long association with many industries have given us the capability to cater to gaseous pollutants that need to be treated from the gases i.e. Particulate matter, Acidic gases (such as SO2, HCl& HF), Oxides of Nitrogen (NOX), Dioxins, Furans and Heavy Metals. Flue Gas Treatment System (FGTS) is the process of removal of gaseous pollutants from the flue gases obtained from various combustion processes.
We at Clair have various solutions to handle different gaseous pollutants & particulate matter (PM).
Alkali reagent is used to neutralize acidic pollutants in the flue gases coming from the boiler. Commonly used alkali reagent is hydrated lime or quick lime. The alkali regent reacts with the acidic pollutants to form salts of calcium (calcium sulphate, calcium sulphite, gypsum and some unreacted lime). Depending on the type of the FGTS system used, the reaction products are either in dry or wet form
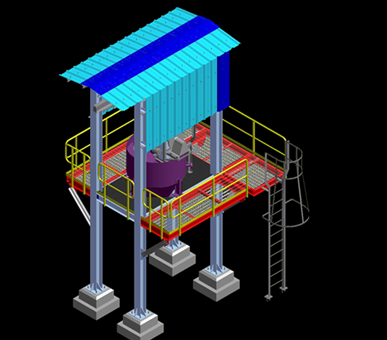
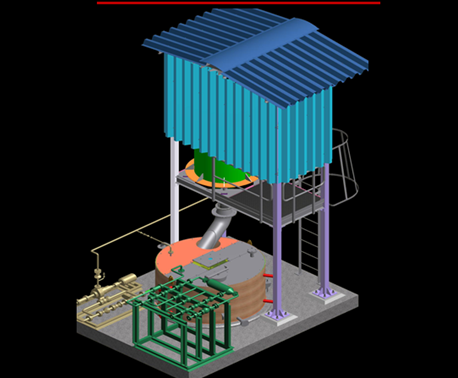
Selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) is a post combustion emissions control technology for reducing NOX The SNCR process reduces NOX through the controlled injection of Urea [CO(NH2)2] solution or Ammonia (NH3) into the flue gas flow to dissociate NOX into nitrogen gas and water vapour. The reagent is injected into a specific temperature zone (8500 to 11500 C) in the boiler. With proper mixing and adequate residence time, the reduction reaction of NOX to harmless molecular nitrogen and water vapour occurs.
Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) is used for the removal of pollutants like Heavy Metals, Dioxins and Furans. The process starts with the injection of PAC before the bag filter inlet whereby the adsorption of pollutants occurs on the filter bag surface.
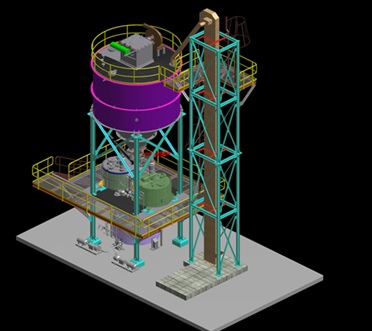
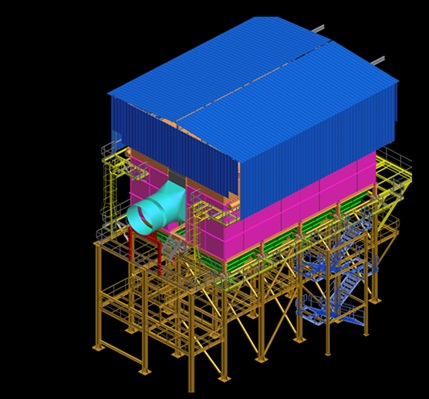
Bag filters are used for the removal of particulate matter. The bag fabric used is of utmost quality and durability especially designed for handling toxic flue gases & respective dust composition.
Our Capabilities:
FGTS systems can be classified into 3 main categories depending on the type of reagent used to capture the pollutants in the flue gasses. They are:
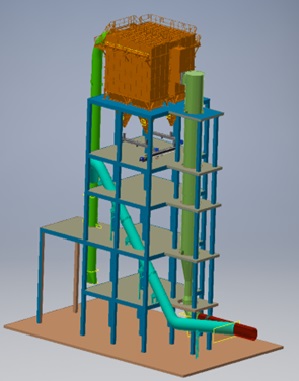
Semi-Wet System
The Semi-Wet System is responsible for the removal of acidic pollutants out of the gaseous phase. The semi-wet system consists of a reactor, followed by bag filter, ID fan and stack. The reagent used to neutralize the acidic pollutants in the gas is first mixed with water to make a solution. The reagent solution is then passed to the reactor. The flue gas enters the semi-wet reactor through a spiral-shaped flue gas inlet channel. A rotary atomizer is located at the top of the semi-wet reactor. This atomizer guarantees atomization of reagent solution and cooling water into fine droplets to create the best contact and temperature conditions for the neutralization of the acid pollutants. The reaction products formed in the reactor are carried downstream to a bag filter. In between the reactor outlet and bag filter inlet, powdered activated carbon is injected in the flue gas flow to absorb heavy metals, dioxins and furans.
Part of the reaction products is removed from the gas flow at the reactor bottom and will be extracted via the lower cone of the residue storage and handling. The second cleaning step takes place on the filter bags in the bag filter, downstream of the semi-wet reactor system.
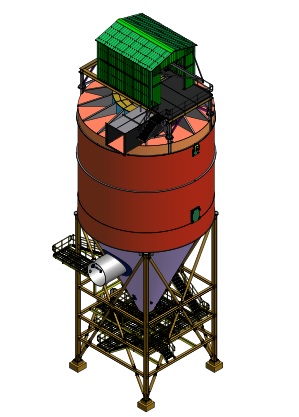




Municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration plants tend to be among the most critical solid waste management options, and they require highly skilled personnel and careful maintenance. For these reasons, incineration tends to be a good choice.
Incinerating municipal solid waste generates large volumes of flue gases. The flue gases carry residues from incomplete combustion and a wide range of pollutants. The pollutants and their concentration depend on the composition of the waste incinerated and the combustion conditions. Ash, heavy metals, and a variety of organic and inorganic compounds can be found in varying quantities
The pollutants are present in the form of particles (dust) and gases such as HCl, HF, and SO2. Some harmful compounds such as mercury, dioxins, and NOx can only be fully removed by applying advanced chemical treatment technologies.
SNCR FOR NOx REDUCTION
The SNCR process is a post combustion NOX reduction method that reduces NOX through the controlled injection of an Urea [CO(NH2)2] solution into the flue gas flow to dissociate NOX into nitrogen gas and water vapour. The reducing agent is injected into the specific temperature zone (8500 to 11500 C), where with proper mixing and adequate residence time for the reduction reaction to occur, NOX is converted to harmless molecular nitrogen.
For the reduction of NOx a 40% urea solution is used as reagent. This solution is prepared in a mixing tank by dissolving urea powder in de-mineralised water, and is then transferred to an storage tank. The injection is done in the first empty pass of the boiler. The urea solution is atomized in the nozzles with air from a local blower. The process of urea preparation, transfer, storage and dosing is described together with the atomizing air supply as SNCR system.
FLUE GAS HANDLING FOR GASEOUS POLLUTANTS
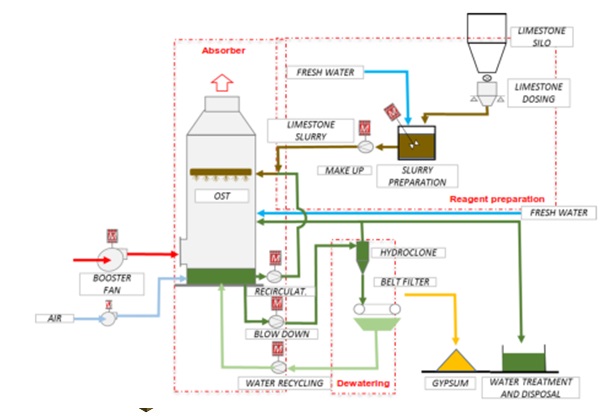
The exhaust flue gases from boiler are led directly into Semi-Wet Reactor. The semi-wet reactor is responsible for the main removal of acids (SO2, HCl & HF). The flue gas coming from the boiler contains fly ashes, the above-mentioned harmful gaseous components and dioxins, furans, heavy metals, mercury & its compounds and others. This flue gas enters the semi-wet reactor through a spiral-shaped flue gas inlet channel. The rotary atomizer is located in the roof of the semi-wet reactor, which atomizes the lime milk and cooling water into fine droplets to create the best contact and temperature conditions for the neutralization of the acid pollutants.
The solid residue is entrained with the flue gas into the downstream bag filter. Part of the residue is removed from the gas flow at the reactor bottom and will be extracted via the lower cone to the residue storage and handling. The second cleaning step takes place on the bags in the bag filter, downstream of the semi-wet reactor.
Immediately after semi-wet reactor, dry Powder Activated Carbon (PAC) will be injected into the flue gas duct and this flue gases are treated in the bag filter where heavy metals and dioxins/furans along with dust will be removed.
The Powder Activated Carbon (PAC) is injected into the flue gas as an adsorbent for dioxins, furans and heavy metals. The system consists of a silo, a dosing hopper with dosing screw, a pneumatic transport system and an injection nozzle. The PAC is injected into the duct just before the bag filter.
| PARAMETERS | UNIT | BEFORE FGTS TREATMENT | AFTER FGTS TREATMENT |
| SO2 | mg/Nm3 | 297 | 32 |
| HCl | mg/Nm3 | 1,200 | 10 |
| HF | mg/Nm3 | 10 | 0.1 |
| NOx | mg/Nm3 | 200 | 200 |
| Dust | mg/Nm3 | 2,500 | 10 |
| Dioxins & Furans | mg/Nm3 | 3.0 | 0.01 |
| Cd, Ti | mg/Nm3 | 0.52 | 0.01 |
| Hg & components | mg/Nm3 | 0.07 | 0.001 |
| As+Pb+ | mg/Nm3 | 8.9 | 0.2 |
Extensively used for boilers those use alternate fuels as well as fossil fuels such as coal / natural gas / oil
Used for medicinal & surgical waste incineration
Scrap rubber incineration plants extensively need complete Flue gas treatment systems
And many others
Our niche expertise and a long association with many industries have given us the capability to cater to three main pollutants that need to be handled from the Flue Gases i.e. Fly ash, Acids / Acid Precursors (SOx, NOx, HCl), Dioxins, Furans & Heavy Metals (Hg).
We at Clair have four types of flue gas treatment equipment designed to handle above gaseous pollutants & particulate matter (PM).
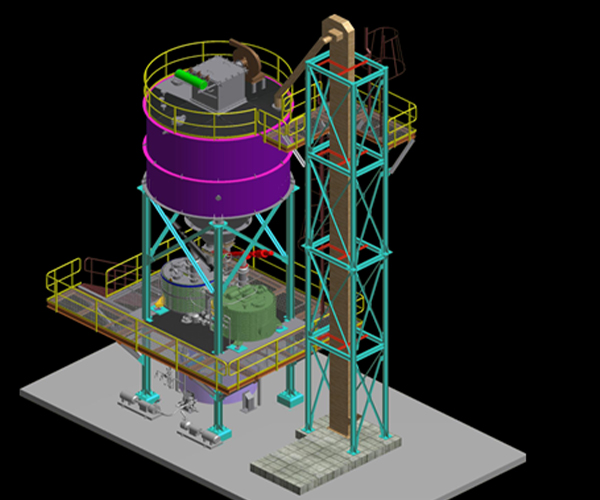
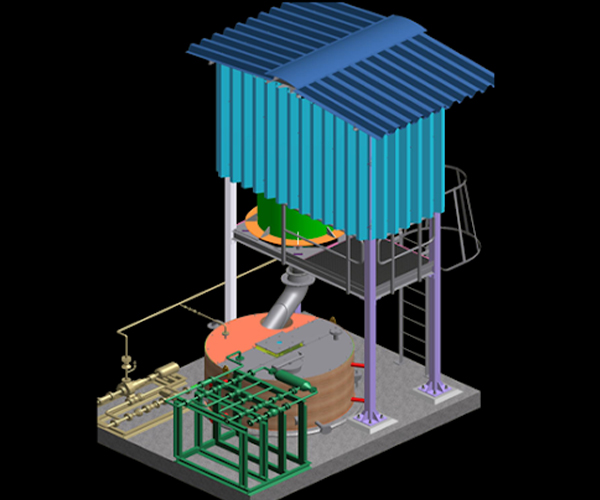
Our AC Injection equipment is used for the removal / collection of elements like Heavy Metals, Dioxins & Furans. The process starts with an injection of Activated Carbon (AC) at the Bag filter Inlet whereby the adsorption of pollutants occurs on the bag surface.

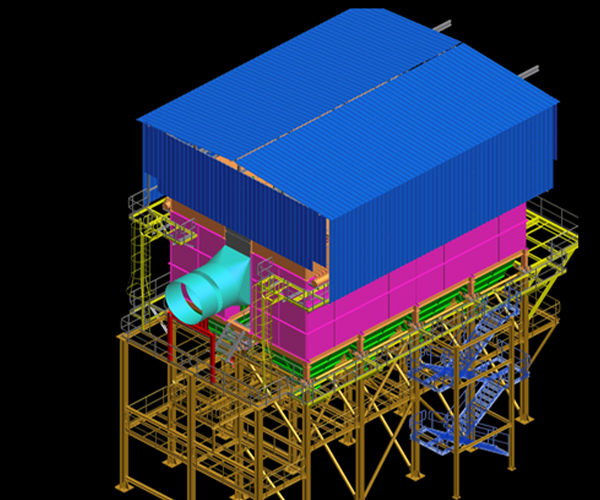




We successfully commissioned a complete turnkey project that constitutes of a 12 MW W2E plant for IL&FS, which is located at Ghazipur, New Delhi in 2016. The plant has been running successfully and is the only plant in India where the fuel is RDF (refuse derived fuel), handling RDF feed of 600 TPD.








Other projects

The spent wash application set up for a client in Karnataka
The top roof with the entire spent wash system for a Client in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka


Installation of the entire plant for ILFS plant at Ghazipur in Uttar Pradesh.